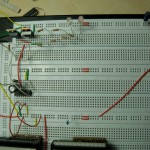
For testing you can take a big capacitor, so that when you manually switch on the high side you see something happen. I took a 330uF capacitor and it is enough to turn the high side MOSFET on for about 30 seconds. Still you have to be careful because the capacitor only gets charged when the low side MOSFET is turned on. So after turning on the power the capacitor is not charged and you have to turn the low side MOSFET on first, then turn it off again and finally switch the high side on.
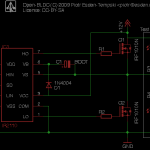
In the final design one should probably select the right bootstrap capacitor. The equation for calculating that value is described on page 6 of the International Rectifier application note AN-978.
You can probably get rid of the capacitor and the diode if you connect VCC directly to VB. The problem you get then is that when the current on VS gets higher then 12V you get a problem. But I may be mistaken. Correct me if I am wrong.
Conclusion: read the damn application notes and I still have problems with understanding the electrical engineer talk! 🙂
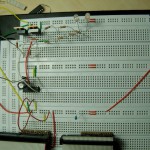
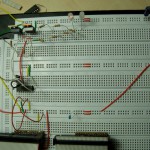
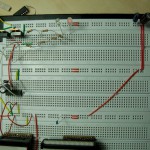
I hope this helps someone. You can see my circuit for one half bridge attached to this post. And a picture of my breadboard.
I use the two LEDs to see what happens with the MOSFETs. They are glowing a little when both sides are off. The one connected to 12V is switching off when the high side is on and the one connected to GND switches off when the low side is on. I love LEDs! 🙂
Cheers Esden
- Circuit
- Powerstage Off
- Low Side On
- High Side On Capacitor Charged
- High Side On Empty Capacitor